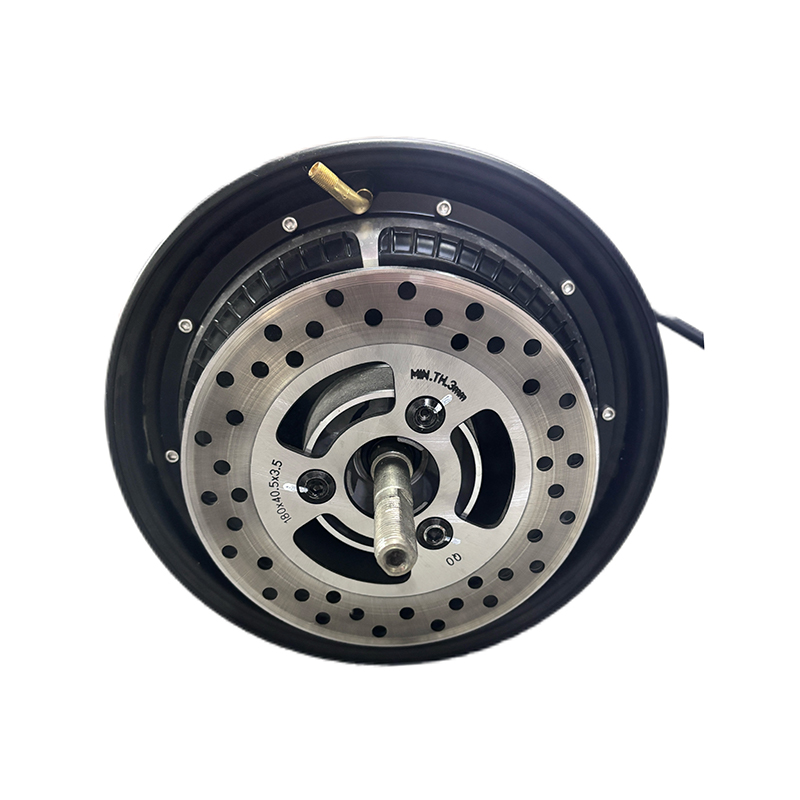
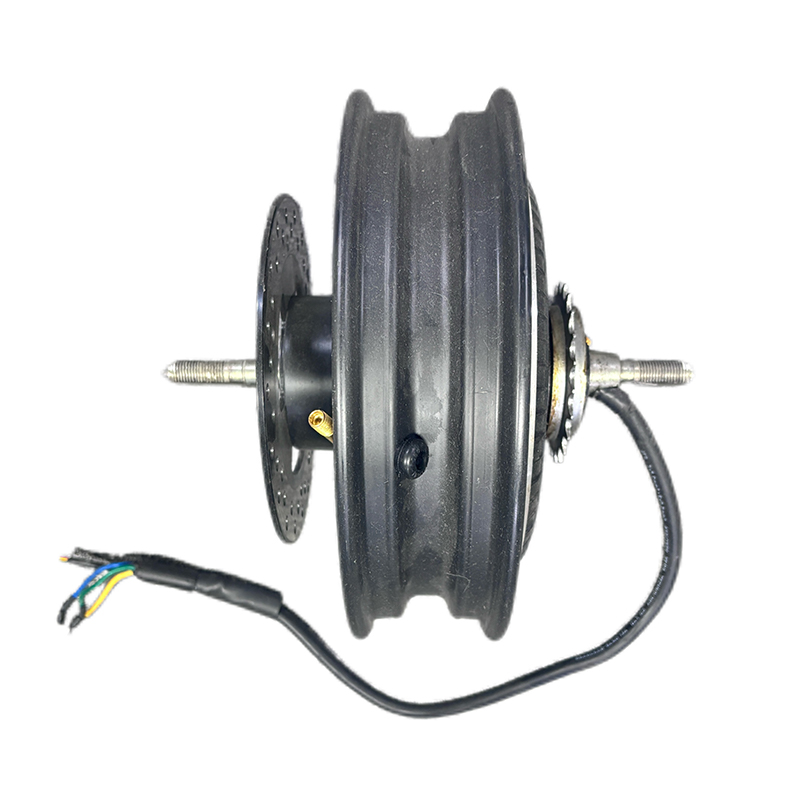
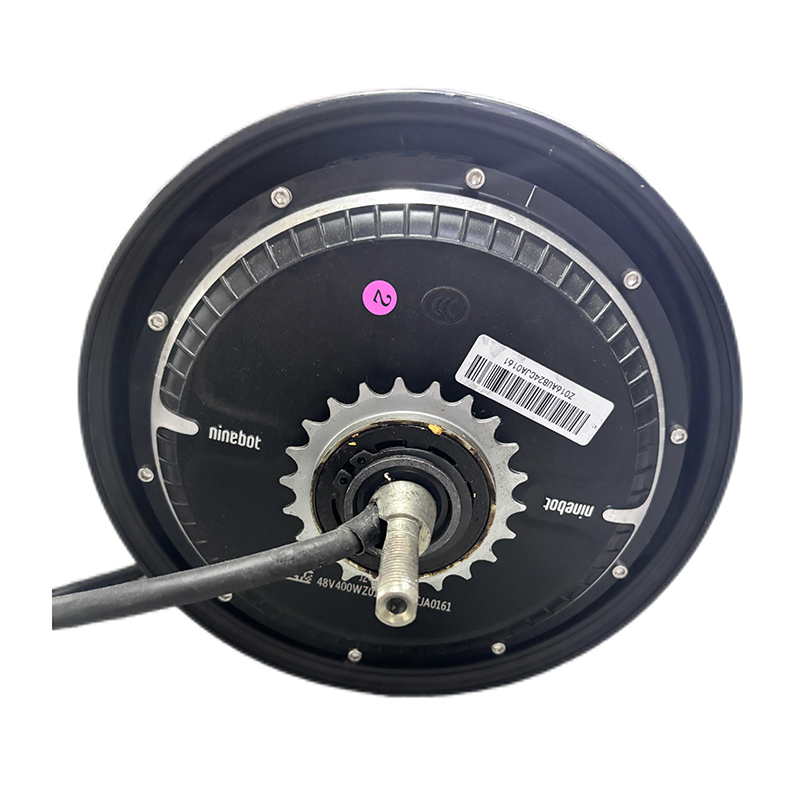
What Makes Mid Drive Electric Motors Superior Mid drive electric motors mount at the bicycle's bottom bracket and directly power the crankshaft, delivering 40-60% better hill-climbing performance and 15-20% greater range compared to hub motors. This central positioning creates optimal weight distri...
READ MOREHub-Motor
B To B business:
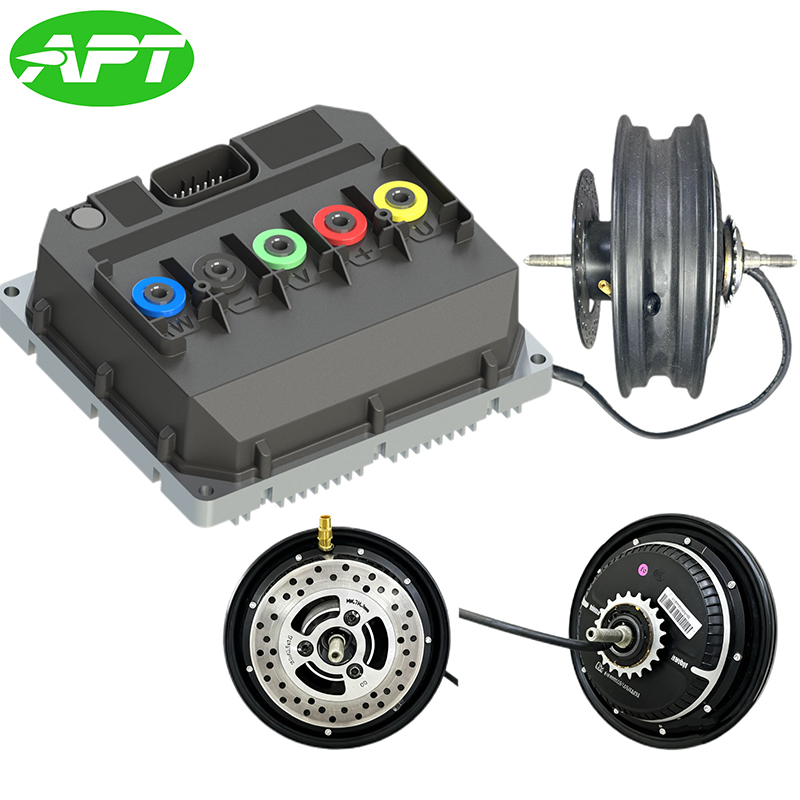
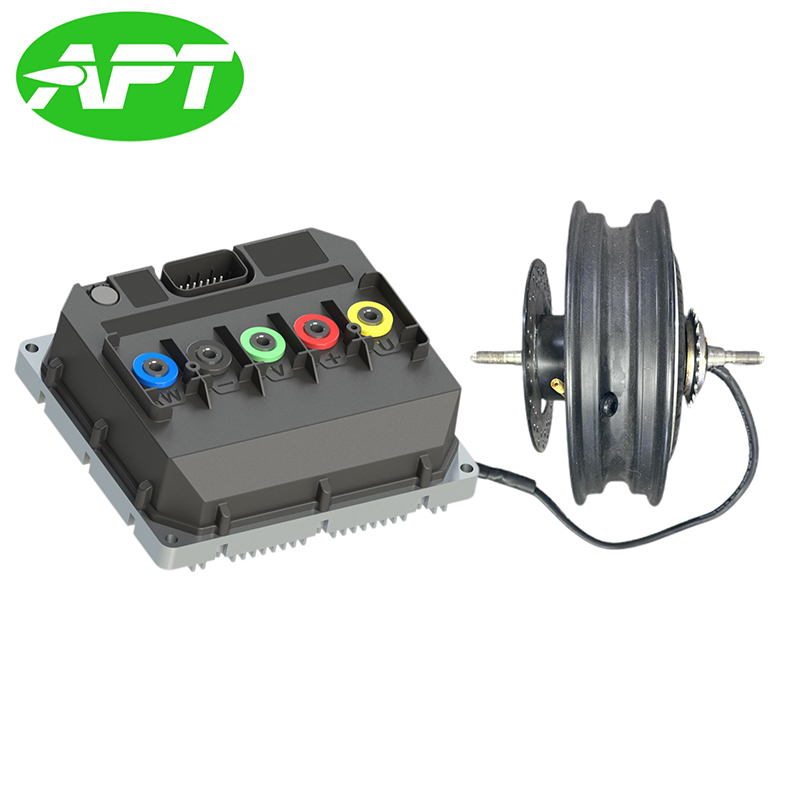
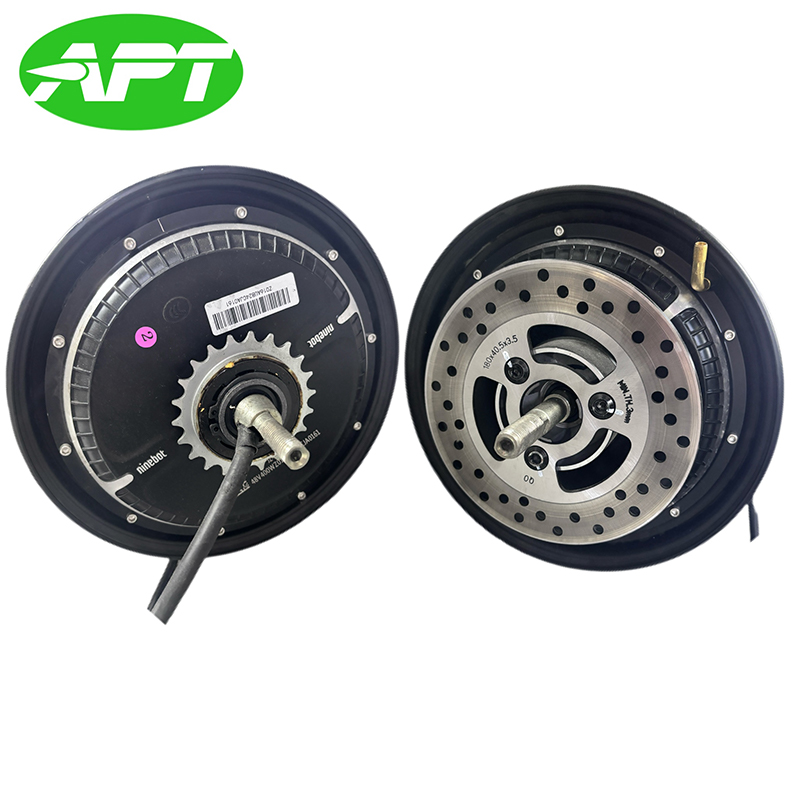
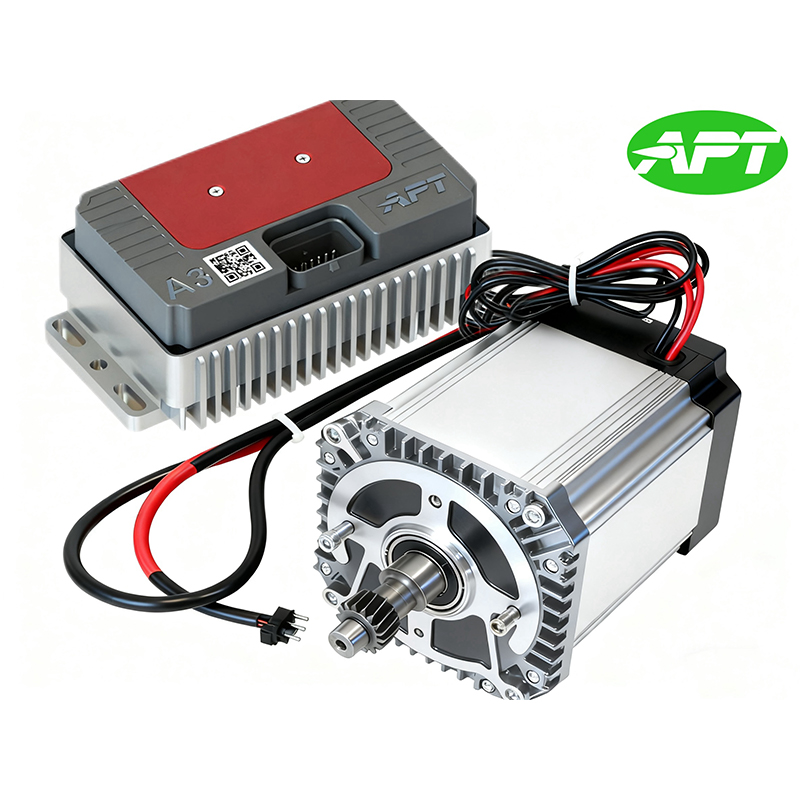
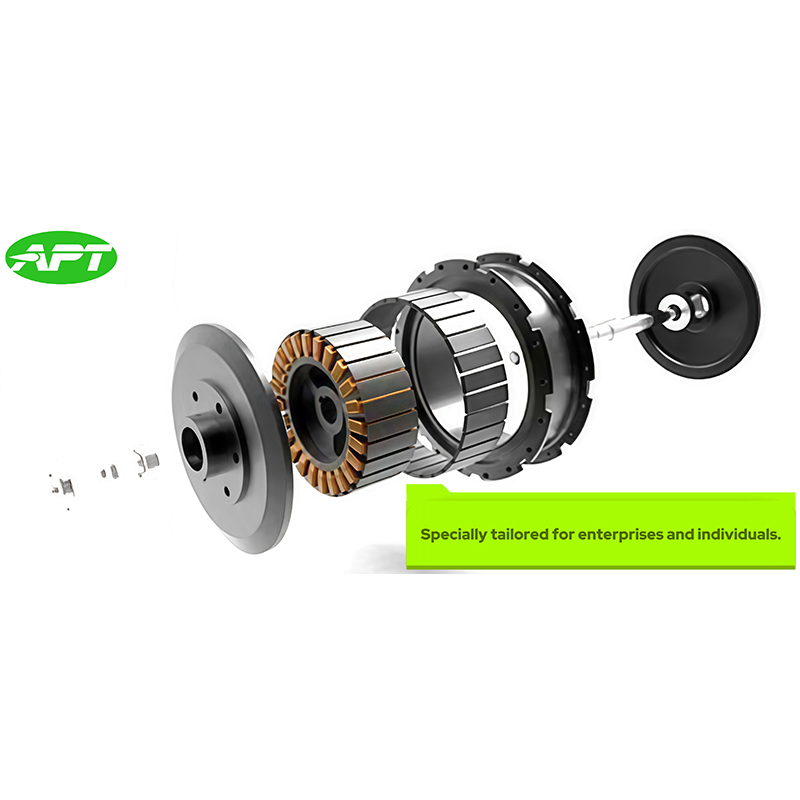
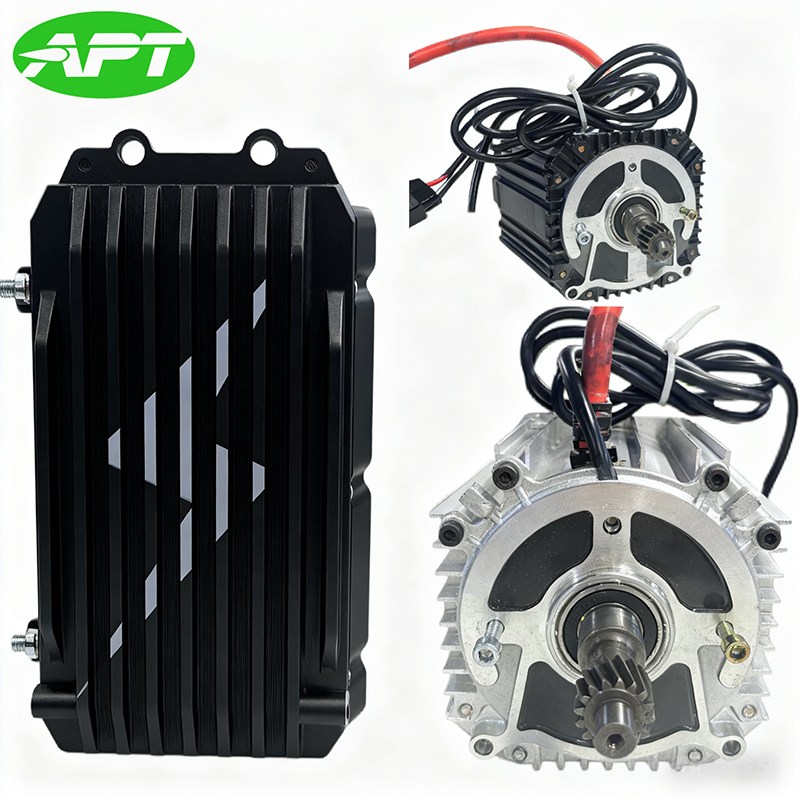
Hub Motor is a drive system that integrates an electric motor directly inside the wheel hub. APT is well aware of the strengths and areas for improvement of various motor brands. In order to provide users with a convenient solution selection, APT often recommends more suitable motor products to customers and packages them together with the controller for sale to customers. They also provide after-sales services for this product to prevent the situation where problems cannot be quickly traced to their root causes when system issues occur.
Technical Parameters
Application&Features
Contact us
| BtoB Product Pairing | ||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
- Individual buyers
- Corporate Procurement
By pressing the "Send" button, you confirm that you give the company your consent for processing your personal data.
Electric Hub Motor Manufacturers
Building on its long-accumulated core motor drive technologies and unique experience in high-power MOSFET parallel connection, Shanghai APT Power Technology Co., Ltd. focuses on providing high-end customers in the industry with core hardware, embedded software for motor drive products, and supporting technical services. Electric Hub Motor Manufacturers in China. Guided by the business philosophy of enhancing the core value of end products, it lays out long-term development strategies to assist customers in their brand growth initiatives.
Over the years, the company has continuously launched high-performance drive control products across various voltage levels, covering application scenarios such as electric motorcycles, electric robot chassis, electric ATVs, UTVs, and electric outboard motors. Custom Wheel Hub Motor Factory. Leveraging mature and reliable product applications, it adheres to better technical solutions and high-quality hardware materials, expanding the market reputation of major complete machine manufacturers by improving user experience.
In the future, the company will continue to deepen its expertise in motor drive technology and focus on fields requiring high quality and reliability. It is committed to becoming a brand benchmark in the motor drive niche industry and creating greater value for various outstanding brands in the new energy power track.
-
-
Mid-drive electric motors—mounted at the bicycle’s bottom bracket, where pedals attach—deliver superior power transfer, hill-climbing ability, and ride balance compared to hub motors, making them the preferred choice for performance e-bikes, cargo bikes, and off-road models. By leveraging the bike’...
READ MORE -
Motor controllers are an essential component in many systems, enabling the precise control of motor performance. As industries advance, the role of software in motor management has become increasingly critical. This article explores the intersection of hardware and software in modern motor controlle...
READ MORE
Industry knowledge
Electric Hub Motors: Advantages and Innovations
Electric hub motors, commonly found in electric bikes, scooters, and even cars, are key components in the growing e-mobility sector. Shanghai APT Power Technology Co., Ltd., established in 2010, specializes in providing advanced drive control solutions for permanent magnet synchronous motors, including hub motors. The company plays a critical role in providing high-performance, reliable, and safe motor solutions for a variety of electrification applications. This section explores the advantages, technological innovations, and applications of hub motors in electric vehicles.
Advantages of Electric Hub Motors
Wheel Hub Motor, positioned in the wheel hub of an electric vehicle, have distinct advantages that make them ideal for certain applications. These benefits contribute to their increasing popularity in the electric mobility market. Key advantages of hub motors include:
- Simplified Design: Hub motors have a straightforward design, with the motor and wheel integrated into one unit. This simplicity reduces the number of moving parts, contributing to fewer maintenance needs.
- Space-Efficient: Since the motor is housed in the wheel hub, there’s no need for additional space to accommodate a traditional motor and drivetrain system, making hub motors ideal for compact, lightweight designs.
- Direct Power Transmission: Hub motors provide a direct transfer of power to the wheels, which increases efficiency and allows for smoother, quieter operation compared to other motor types.
- Minimal Mechanical Losses: Hub motors are free from mechanical losses that occur in traditional motor systems where power is transmitted through chains, belts, or shafts, contributing to better overall efficiency.
- Reduced Maintenance: With fewer moving parts and no need for complex gearing systems, hub motors typically require less maintenance compared to mid-drive motors or traditional combustion engines.
Challenges in Electric Hub Motor Design
While hub motors offer several advantages, their design and implementation come with specific challenges that must be addressed to maximize performance and longevity. Some of the main challenges include:
- Heat Dissipation: Hub motors, due to their location in the wheel, are subject to limited cooling options. Managing heat effectively during prolonged use, particularly in high-demand situations like climbing hills, is crucial for preventing overheating.
- Weight Distribution: Although hub motors are space-efficient, their location in the wheel can affect the weight distribution of the vehicle. In two-wheeled electric vehicles, an imbalance in weight distribution can impact handling and ride quality.
- Limited Torque Control: Hub motors typically do not offer the same level of torque control as mid-drive motors. This can be limiting for certain types of riding, such as mountain biking or cargo hauling, where variable torque is needed.
- Efficiency at High Speeds: While hub motors perform well at lower speeds, their efficiency may decrease at higher speeds, particularly in vehicles designed for long-distance travel. This can impact range and overall performance.
- Integration with Suspension Systems: In some designs, integrating hub motors with suspension systems can be challenging. For optimal ride comfort, suspension and motor systems need to be synchronized, which requires precise engineering.
Technological Innovations in Hub Motors
As electric mobility continues to evolve, innovations in hub motor technology are pushing the boundaries of performance, efficiency, and design. These advancements are addressing some of the challenges mentioned above and enhancing the overall capabilities of hub motors. Some key technological innovations include:
- Advanced Cooling Techniques: New cooling systems, such as integrated liquid cooling or advanced heat sinks, are being used to enhance heat dissipation and prevent overheating in hub motors.
- Improved Power Density: Modern hub motors feature increased power density, meaning they can provide higher levels of power in smaller, more compact designs. This innovation is especially useful for electric bikes and scooters where space and weight are limited.
- Regenerative Braking Systems: Many hub motors are now being equipped with regenerative braking capabilities, allowing the motor to capture energy during braking and feed it back into the battery, improving overall energy efficiency and extending range.
- Wireless Communication and IoT Integration: IoT-enabled hub motors allow for real-time monitoring of motor performance, battery health, and other key metrics via smartphone apps, providing users with more control and insight into their vehicle’s condition.
- Customizable Power Settings: Innovations in controller technology are allowing users to adjust the power output of hub motors based on riding conditions, rider preferences, and terrain, enhancing the riding experience.
Applications of Hub Motors in Electric Vehicles
Electric hub motors are used across a wide range of electric mobility applications, from electric bicycles to e-scooters and electric cars. Their simple, efficient design makes them particularly well-suited for the following applications:
Electric Bicycles
Hub motors are commonly used in electric bicycles, offering a quiet and efficient way to power the bike without the need for complex mechanical systems. Hub motors are well-suited for urban commuting, recreational cycling, and light off-road riding. Their simplicity and low maintenance requirements make them a preferred choice for many ebike models.
Electric Scooters
In electric scooters, hub motors are used for their compactness and efficiency. These motors are well-suited for light urban transportation, offering a simple solution for short-distance travel. Hub motors in scooters help keep the vehicle lightweight, making them easy to handle and maneuver in city environments.
Electric Cars
While hub motors are most commonly used in two-wheeled electric vehicles, they are also being explored for use in electric cars. Hub motors in electric vehicles can provide an all-wheel-drive system by using a separate motor in each wheel, improving performance and efficiency. However, this application is still in the experimental phase and faces challenges related to weight, power delivery, and vehicle handling.
The Future of Hub Motors in Electric Mobility
Looking ahead, the future of electric hub motors is promising, with continued innovation driving advancements in efficiency, power output, and integration. Key trends that are likely to shape the future of hub motors include:
- Increased Integration with Smart Technologies: As electric vehicles become smarter, hub motors will integrate more with cloud-based systems, allowing for remote diagnostics, predictive maintenance, and personalized performance settings.
- Focus on Sustainability: Future hub motors are expected to incorporate more sustainable materials and energy-efficient designs, contributing to the growing demand for eco-friendly transportation solutions.
- Enhanced Performance in Urban Mobility: With the rise of urban micro-mobility solutions, hub motors will continue to evolve to provide better performance in urban environments, offering higher torque, greater efficiency, and faster acceleration.
- Improved Cost Efficiency: As the technology matures, the cost of hub motors will decrease, making them an even more accessible option for manufacturers and consumers, especially for budget-friendly electric mobility products.

 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى